Tools
Abt Global has created or supported a number of innovative tools to answer difficult questions, such as:
- What are the health and financial benefits of improving air quality?
- What are the environmental impacts of large-scale changes to the United States economy?
- How can we ensure standardized results reporting from randomized control trials and other impact evaluations?
Abt tools such as The ASPES Learning Portal, CommentCounts™, EVIRATER™, DART, Cost Benefit Analysis Workbook, PovertyCounts™, Principal Stratification Tool, Solid Waste Emissions Estimation Tool (SWEET), and SPI-Path and its suite of tools are all software-based systems that are informing governments, citizens, and others of challenges people are facing today, and may face tomorrow.
AMEE (Abt Monitoring and Evaluation Ecosystem)
.jpg)
The Abt Monitoring and Evaluation Ecosystem (AMEE) supports project monitoring, evaluation, and learning (MEL) data management needs. AMEE is an ecosystem of easily accessible and vetted technologies that enables projects to engage more strategically with routine monitoring data and turn those data into insights.
AMEE offers an in-house expert team, a complete set of replicable processes, and a fully functional MEL ecosystem for data collection, data management, and basic analytic and visualization needs. With AMEE, teams and clients can stay nimble and focus on strong system governance, data exchange, and interoperability to help innovate and grow where needed. Want to learn more? Contact: amee@abtassoc.com.
Climate HealthCounts™

Abt’s Climate HealthCounts™ takes readily available data from governments’ existing climate action planning to generate estimates of the public health benefits that result from air quality improvements. The tool:
- Models air quality improvements resulting from reductions in air pollution emissions.
- Quantifies the public health benefits of improved air quality, such as fewer hospitalizations, emergency department visits, and premature deaths.
- Determines the monetized value of those health benefits.
- Creates accessible outputs, including maps to analyze how benefits are distributed throughout the state or region, and charts to summarize the equity impacts of the benefits.
Contact David Cooley to learn more.
CommentCounts™
CommentCounts™ is a proven, secure, web-based tool for complex rulemaking support. Federal agencies use this tool to manage public comments and respond meaningfully and systematically. With CommentCounts, comments and responses are saved and managed in a secure, online database. Content specialists can customize the database to meet task requirements and code and organize comments into issue categories. CommentCounts handles multiple comment formats and is fully searchable. Reports can be customized and generated in Microsoft Word and Excel formats. For more information or to set up a demo, contact Frank Divita.
Cost Benefits Analysis (CBA) Workbook

As the technical lead of the USAID-funded CEADIR project, Abt developed a spreadsheet (.zip) for analyzing the costs and benefits of USAID’s investment in mangrove restoration in and around the port city of Quelimane, Mozambique. CBA Workbook builds on our coastal restoration analyses and support in the United States and worldwide. Users can adapt this spreadsheet to their own related work comparing the net benefits of mangrove restoration projects to investments in hard infrastructure that reduce coastal erosion, flooding, and associated damages caused by storm surges. The spreadsheet can also evaluate other financial and economic benefits of mangrove restoration, such as fish production and carbon sequestration. For more information, contact BDU@abtassoc.com.
DART

Impact evaluations – and randomized control trials in particular – are the core of Abt’s evaluation work. To reduce our time and costs and increase the clarity and consistency of evaluation results, we developed the Data Analysis and Reporting Tools (DART) after recognizing the potential benefits of a standardized analysis and reporting system. DART provides guidance and software code for statistical impact analysis, as well as code for producing publication-ready tables displaying results from that analysis. For more information, contact Dan Litwok.
Digital TA Marketplace

Abt’s Digital TA Marketplace is an ecosystem of digital tools designed to support the wide range of services included in the scope of technical assistance (TA)—from the creation and publishing of best practices, to learning pathways, and performance assessments. Tools and services within the digital ecosystem are aligned to meet the needs of individuals delivering and receiving TA and are integrated so that data can be collected across the program lifecycle and the impact of TA services can be monitored, measured, and improved.
Base functionality within the TA Marketplace includes a suite of intelligent digital services—including process modeling, forms digitalization, business rules, and a decision engine—all of which can be used to automate and speed processes. Robotic process automation can reduce costs and error in repetitive tasks. Additionally, the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning can help ingest and analyze data from a variety of sources, including uploaded reports, emails, or comments. For more information, contact BDU@abtassoc.com.
DIME (Data Integration Management Ecosystem)
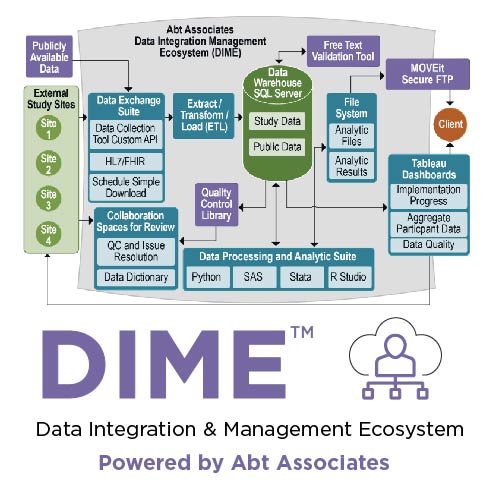
Abt’s Data Integration and Management Ecosystem (DIME) is a HIPAA- and FISMA Moderate-compliant suite of interoperable tools that can process hundreds of millions of data points while assuring data quality. Components of DIME include:
- Data integration layer for automatically downloading, transforming, and merging data in multiple formats and protocols
- Central data warehouse for tracking and versioning raw, intermediate, and final datasets
- Library of more than 250 standard quality checks
- Free-text review tool that streamlines reviews of free-text fields
- Analytic file development library, which enables rapid construction of analytic files while retaining the derivations history
- More than 50 dashboard templates that monitor all aspects of study implementations.
For more information contact Brian Sokol
Eva
HUD has released Eva, the latest in a series of Abt-designed tools. The open-source project is intended to help local Homeless Management Information Systems (HMIS) Administrators in Continuums of Care (CoCs) around the U.S. assess the accuracy and completeness of their data and resolve issues. Eva is a cloud-based update of an Excel-based tool, and the shift to a web-based platform has allowed for increased accessibility to data, increased cloud-based processing power, better version control, and more transparency in the reporting. Additional upgrades, such as the ability to measure inflow, outflow and how many people have attained housing, are planned. For more information, contact Jesse Jorstad.
Evaluation Technical Assistance (TA) Tools

Our Evaluation TA team uses these tools to help hundreds of evaluators design and conduct independent evaluations of programs, interventions, and practices aimed at improving people’s lives. Evaluations that provide rigorous and actionable evidence start with careful planning. Our tools help evaluators design and conduct evaluations of a project’s impact and fidelity of implementation while anticipating common pitfalls.
Our tools include The Evaluation Design Summary Template, which guides evaluators through the process of fully articulating their evaluation plan; the excel based Analytic Contrast Tool to detail each analysis; and The Fidelity of Implementation Matrix, a step-by-step tool to create a fidelity of implementation measure.
For more information about our Evaluation TA tools, contact Beth Boulay.
EVIRATER™

Policymakers, program leaders and philanthropic organizations are increasingly demanding that decision-making about policies and programs be guided by evidence. However, few tools are available to assess the quality of the full range of evidence produced by the spectrum of research designs typically used to evaluate program effects.
Abt is responding to this need with EVIRATER™, a system for rating the strength of evidence that can be applied to the full range of designs that might be used to evaluate programs. EVIRATER™ expands on current rating systems such as the What Works Clearinghouse and Clearinghouse of Labor Evaluation and Research that are used to review more rigorous research designs, such as randomized controlled trials and high quality quasi-experimental studies. For more information, contact Cris Price or Barbara Goodson.
PovertyCounts™

PovertyCounts™ is used to help development program staff estimate the extent to which their programming is reaching target groups and changing the poverty rate over time. The tool is designed to be faster to administer than previous tools, tailored to specific country or sub-country contexts, and sensitive to changes in the economic status of program participants. PovertyCounts™ rapidly analyzes information from sampled households, applying a model developed from existing consumption data to estimate the poverty rate among program participants and the degree of confidence surrounding that estimate. For further information about the PovertyCounts™, please contact Anthony Leegwater.
Solid Waste Emissions Estimation Tool (SWEET)

The Solid Waste Emissions Estimation Tool (SWEET) is designed to quantify emissions of methane, black carbon, and other pollutants. The tool can track greenhouse gasses from a range of sources in the municipal solid waste sector, including landfills, waste collection fleets, and garbage burning. The data collected by SWEET helps solid waste managers establish and analyze baseline emissions and evaluate future scenarios (e.g., upgrading an open dump to a managed dumpsite, or transitioning from diesel-based collection vehicles to ones that use compressed natural gas). The tool was developed by Abt --with support from SCS Engineers--on behalf of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and the Climate & Clean Air Coalition. For more information, contact Joe Donahue.
SPI-Path

The Social Policy Impact Pathfinder (SPI-Path) is a suite of tools that offers policymakers in the government and philanthropic sectors the opportunity to learn which aspects of a policy or program contribute most to its effectiveness. SPI-Path provides researchers with the blueprint for how to identify the influence of the individual components of social programs. Through these resources, which include working examples, statistical software code, and references in peer-reviewed journals, SPI-Path makes answering questions related to “what works?” easy and defensible. SPI-Path’s suite of tools includes SPI-Path Individual, Site and Factor. Download SPI-PATH user guides.
Two additional tools are useful to pair with SPI-Path:
ASPES Learning Portal
The Analysis of Symmetrically Predicted Endogenous Subgroups (ASPES) Learning Portal is another tool for understanding the impact of an intervention on “endogenous subgroups” using experimental evaluation data. Endogenous subgroups are those that are defined by events that occur after the point of random assignment. For example, program managers and evaluators may be interested in whether the impact of an intervention is larger for the subgroup of study participants who experienced more of the intervention (and possibly smaller for those who experienced less of it). The ASPES Learning Portal provides instruction on two versions of the ASPES method: a discrete version that allows researchers to estimate impacts on discretely defined subgroups and a continuous version that allows researchers to estimate the relationship between a continuously defined endogenous variable and impact magnitude.
Principal Stratification Tool
The Principal Stratification Tool is a website that guides researchers through (1) determining whether a principal stratification framework is appropriate for their data and research questions and (2) calculating bounds for the causal effects of treatment within the specified strata. Principal stratification is a useful framework for identifying subgroups and defining principal causal effects of interest, which are computed from data generated by a randomized controlled study. However, estimating principal causal effects is challenging and requires multiple assumptions. An alternative solution promoted by this tool is to generate bounds for the principal causal effects. This tool guides researchers through the framing, assumptions and calculations necessary to estimate the bounds on stratum-specific treatment effects. For more information, contact Shawn Moulton.
Virtual Omnichannel Integrated Citizen Engagement (VOICE)

Government agencies are modernizing how data is collected, stored, and used to generate evidence that informs policy making and implementation. At the same time, in a digital age, government-to-citizen communication requires continuously connecting people to the information they need, while simultaneously collecting reliable data from live interactions across multiple communication channels that link people to services, answer questions, or share and collect information during emergencies. Abt developed a solution to this complex problem.
Abt’s Virtual Omnichannel Integrated Citizen Engagement (VOICE) solution provides agencies with the ability to collect data through two-way, multi-channel systems. VOICE is an interconnected eco-system of skilled people and cloud-based technologies. It facilitates two-way information sharing and gathering across a range of channels and media, including mobile apps, web, text, video, email, telephone, traditional mail, and even in-person. This combination of human intelligence and advanced technological solutions maximizes operational efficiency while ensuring high quality information that positions agencies for success.
The VOICE ecosystem of interconnected platforms supports efforts of all sizes and can scale easily, enabling agencies to conduct everything from targeted outreach to large, complex surveys. It connects multiple technology platforms such as those for complex survey research efforts (e.g., Confirmit and REDCap), inbound communication systems (e.g., Sytel), and platforms for mobile apps, web-based portals, sophisticated interactive voice response (IVR), email, and SMS text response.
